Each configuration file belongs to one SPOT project, if the same basename is
used for corresponding files.
SPOT uses
simple text files as interfaces from the algorithm to the statistical tools.
- The user has to provide the following files:
- (i)
- Region of interest (ROI)
files specify the region over which the algorithm parameters are tuned.
Categorical variables such as the recombination operator in ES, can be
encoded as factors, e.g., ``intermediate recombination'' and ``discrete
recombination.''
- (ii)
- Algorithm design (APD) files are used to specify parameters
used by the algorithm, e.g., problem dimension, objective function, starting
point, or initial seed.
- (iii)
- Configuration files (CONF) specify SPOT specific parameters,
such as the prediction model or the initial design size.
- (iv)
- Meta files (META) specify parameters from the problem design. The algorithm is separately tuned
for each setting of the meta parameters. For example, consider tuning a (1+1)-ES on the sphere function for
varying problem dimensions, say
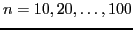 . The problem dimension
. The problem dimension 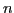 is a meta parameter
in this case.
is a meta parameter
in this case.
- SPOT will generate the following files:
- (i)
- Design files (DES) specify algorithm designs. They are
generated automatically by SPOT and will be read by the optimization algorithms.
- (ii)
- After the algorithm has been started with a parametrization from the
algorithm design, the algorithm writes its results to the result
file (RES). Result files provide the basis for many statistical
evaluations/visualizations. They are read by SPOT to generate prediction models. Additional prediction
models can easily be integrated into SPOT.
- (iii)
- During the meta mode, the algorithm is tuned on several problem instances. The best configuration from each
problem instance is written to the final best solution file (FBS).
bartz
2010-08-24